What a season it has been. I hope and pray that each individual and family member receiving this note is healthy and safe. My goal over the coming months is to increase the volume of written communication. These notes will not replace our regular scheduled tax, planning, or portfolio updates. Instead, they will supplement those conversations and provide a financial perspective that can be communicated efficiently in writing. The purpose of this note is to discuss our position on market timing and portfolio rebalancing.
Portfolio Rebalancing
We believe that the financial plan is the seminal document for investors seeking to accomplish long term goals. Each financial plan is prescriptive in the amount of saving and portfolio return that is required to accomplish the goals outlined in the plan. The asset allocation decision is an important one—given it considers risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial goals[1].
The goal of rebalancing is to minimize risk and recalibrate, rather than to maximize return. The process of rebalancing takes the imbalance that is created by certain asset classes over time and recalibrates those asset classes. It takes the asset allocation that was originally prescribed by the financial plan and reorients the portfolio to its intended mix of stocks, bonds, and cash.
For most portfolios, recalibration should occur a few times a year. This is particularly true in retirement accounts, given there is no tax liability for creating gains. In trust accounts as well as individual and joint accounts, there is a sensitivity to tax gains as a possible consequence of rebalancing. Every effort is taken to minimize tax liability in those types of accounts. However, it can be hazardous to let the concern over taxes negate the discipline of regularly rebalancing. I can think of too many instances where a client avoided rebalancing their account out of concerns for taxes—only to have the market go down. The tax liability for rebalancing was ultimately dwarfed by the loss of principle due to the market decline. In short, it is rarely advisable to let the tax tail wag the investment dog.
Market Timing
The most common question I receive is, “when should we sell out?” My typical response is never. If an investor has a financial plan, which accounts for planning-based return expectations and subsequent asset allocation, the portfolio should always be properly positioned for risk and return. If the goal of “selling out” is to reduce risk, the action of selling implies the original allocation was incorrect.
In the past, there have been a few occasions where dramatically reducing risk by selling equities and raising cash makes sense. Or, to sell a portion of the stock investment and place the proceeds in bonds. But those reasons have to do with new information about the client situation, which prompt a change in the asset allocation. As an example, years ago, we had a client let us know that their business was struggling, resulting in the potential that their retirement account would need to be tapped for an emergency. Liquidating equities in their account was a response to a change of plans and circumstances—this is a plan modification and not market timing.
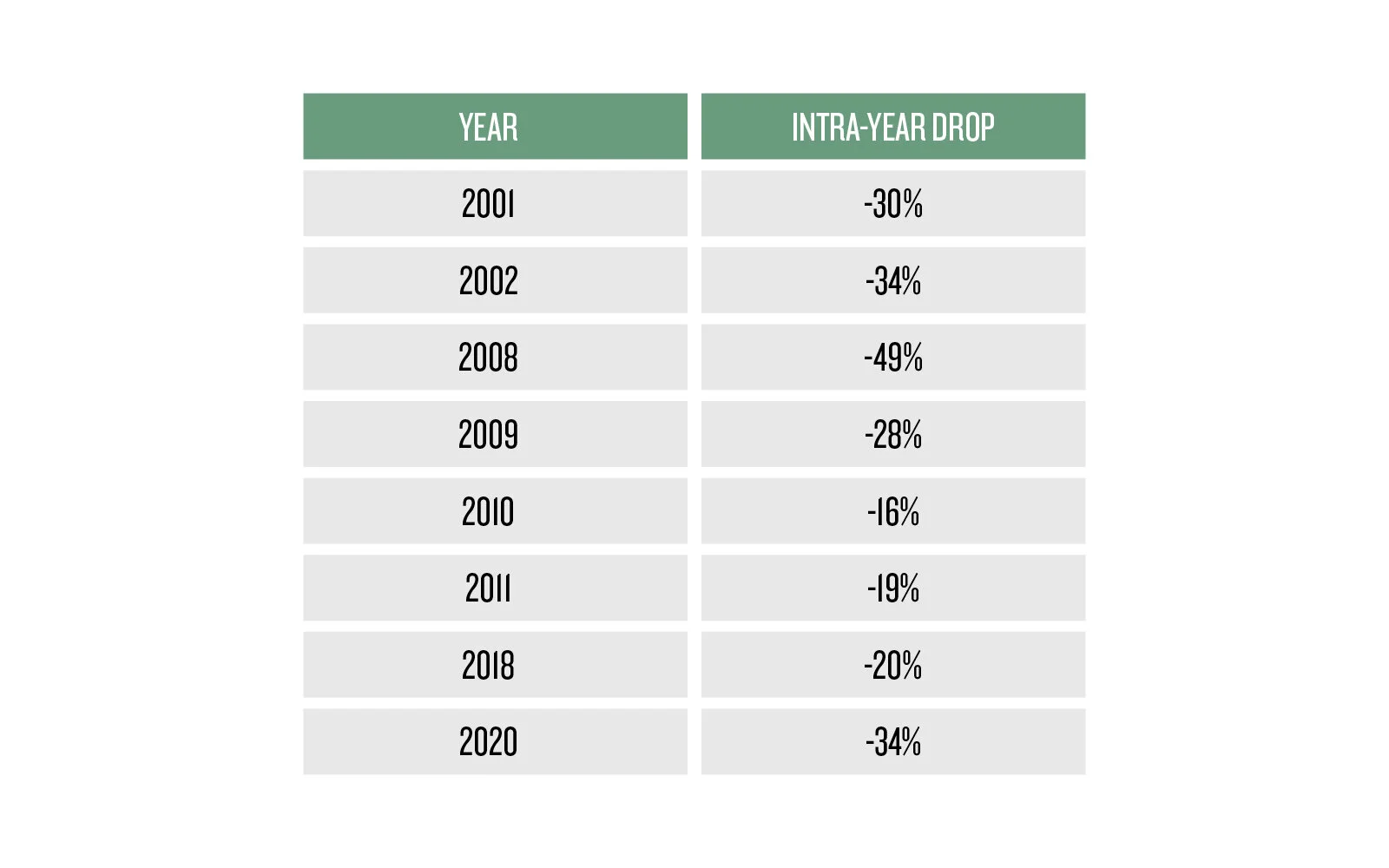
There is ample research dating back to the 1980s which suggests timing the market[2] or being able to predict the direction of the market is challenging at best[3]. Therefore, we believe in rebalancing “to recapture the portfolio’s original risk-and-return characteristics”[4], and we rely on the financial plan as the authoritative document to prescribe the proper mix of stocks and bonds for each client we serve.
Sources
[1] Zilbering, Y., Jaconetti, C. M., & Kinniry Jr, F. M. (2015). Best practices for portfolio rebalancing. Valley Forge, Pa.: The Vanguard Group. Vanguard Research PO Box, 2600, 19482-2600.
[2] Brinson, G. P., Hood, L. R., & Beebower, G. L. (1986). Determinants of portfolio performance. Financial Analysts Journal, 42(4), 39-44.
[3] Butler, A. W., Grullon, G., & Weston, J. P. (2005). Can managers forecast aggregate market returns?. The Journal of Finance, 60(2), 963-986.
[4] Zilbering, Y., Jaconetti, C. M., & Kinniry Jr, F. M. (2015). Best practices for portfolio rebalancing. Valley Forge, Pa.: The Vanguard Group. Vanguard Research PO Box, 2600, 19482-2600.